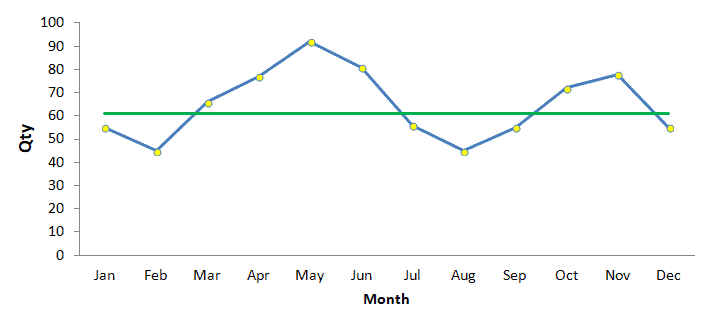
When to Use a Run Chart
A run chart is used to track performance over time, identifying trends and patterns for improvement. It is beneficial for continuous monitoring and quality improvement initiatives.
By visualizing data in a simple format, organizations can easily detect shifts and variations, enabling timely interventions for process enhancement. Utilizing a run chart can help teams identify root causes of issues and make informed decisions based on factual data trends.
Whether in healthcare, manufacturing, or service industries, the insights gained from a run chart can drive sustainable improvements and optimize outcomes. Embracing this tool fosters a culture of data-driven decision-making, paving the way for ongoing success and efficiency.
Credit: www.skymark.com
When To Use A Run Chart
Using a run chart can be a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data trends over time. This type of chart is particularly useful in process improvement efforts, enabling organizations to monitor performance, identify patterns and trends, and make continuous improvements. In this article, we will explore three key scenarios where utilizing a run chart can lead to better decision-making and ultimately drive positive outcomes.
Monitoring Process Performance
Running a business involves numerous processes, and monitoring their performance is crucial for both short-term troubleshooting and long-term optimization. With a run chart, organizations can easily track process metrics and observe any variations or deviations from the norm. By graphing the data points over time, trends and patterns can become evident, making it easier to identify issues and take prompt action. The visual representation allows stakeholders to grasp the situation at a glance, facilitating effective communication and collaboration.
Identifying Trends And Patterns
Patterns and trends have a significant impact on process outcomes, and spotting them early can help organizations stay ahead of problems and capitalize on opportunities. Using a run chart, you can detect recurring patterns or trends that may not be apparent from simply examining raw data. By establishing a baseline and plotting subsequent data points, you can quickly analyze whether changes are random or indicative of actual trends. This proactive approach empowers organizations to respond promptly to emerging trends, making better-informed decisions for the future.
Making Continuous Improvements
In any organization, continuous improvement is key to achieving operational excellence and remaining competitive. A run chart provides a visual representation of process data, making it easier to identify areas for improvement. By closely monitoring the chart, organizations can pinpoint whether implemented changes have a positive impact or need further refinement. This process enables the identification of bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or suboptimal practices that hinder performance. Armed with this knowledge, organizations can implement targeted improvements, drive change, and optimize processes to reach new levels of productivity and efficiency.
Key Metrics For Run Charts
Run charts are crucial for tracking key metrics over time, highlighting trends and patterns. They are used to identify when a process is stable or when a change occurs. Utilizing run charts helps in determining the appropriate time for implementing improvements and monitoring their impact.
Selecting The Right Metrics
Choosing relevant metrics is the first step for an effective run chart. Metrics should be important, measurable, and directly impact the process. Consider customer satisfaction, production time, or defect rates.Data Collection And Organization
Accurate data collection is crucial for a meaningful run chart. Organize the data in a systematic and clear format for analysis. Maintain consistency in collecting data to ensure reliability. Ensure appropriate tools are used for reliable data collection. Use data visualization to facilitate easy interpretation. Table: Sample Metrics for Run Charts | Metric | Description | |———————-|—————————————————-| | Customer Satisfaction| Percentage of satisfied customers | | Production Time | Time taken to complete a task | | Defect Rates | Number of defects per product | | Sales Revenue | Total revenue generated from sales | | Website Traffic | Number of visitors to the website |- Choose metrics that matter to the process.
- Ensure data is collected accurately and consistently.
- Organize data systematically for easy analysis.
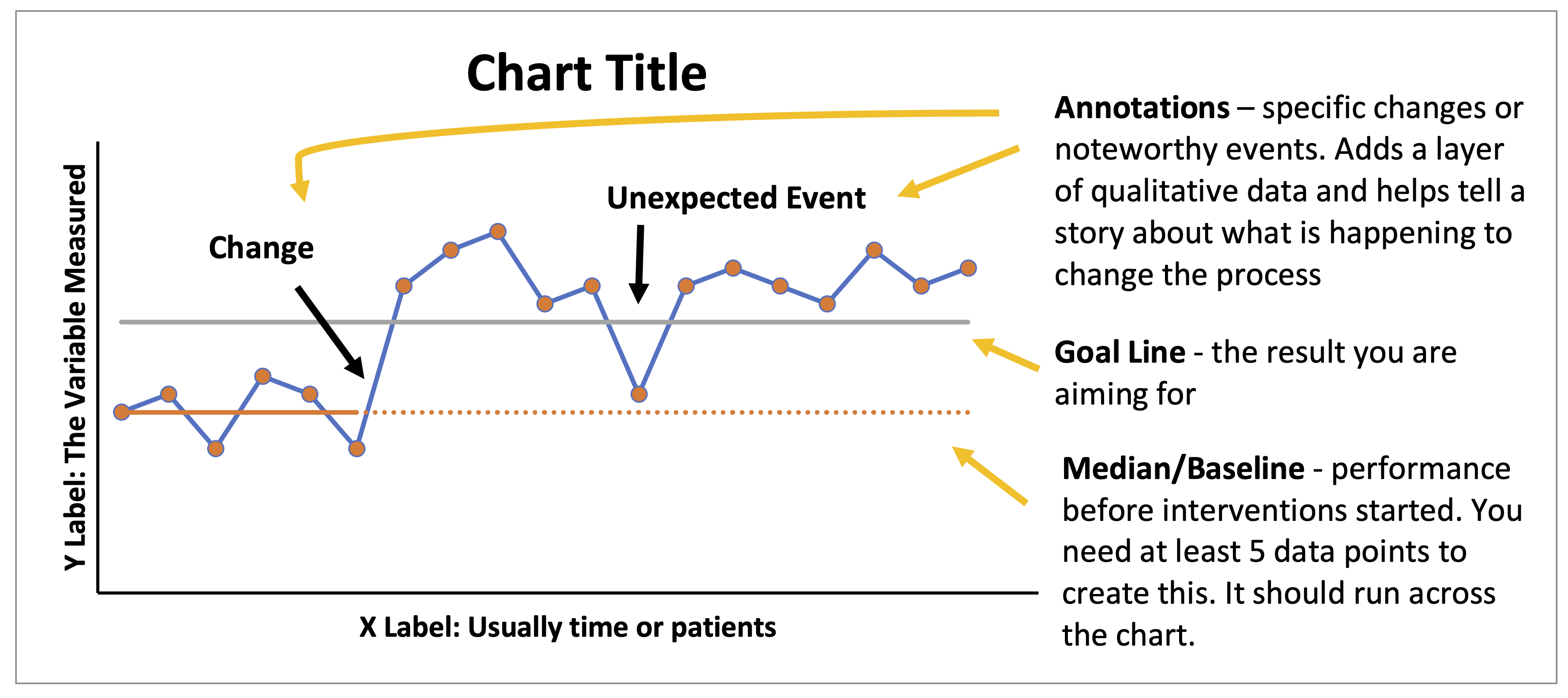
Creating An Effective Run Chart
Choosing The Appropriate Time Frame
Consider your analysis goals when determining the time frame for the run chart.
Plotting Data Points Accurately
Ensure precise recording of data points to maintain the integrity of the chart.
Credit: thecompletemedic.com
Interpreting Run Chart Results
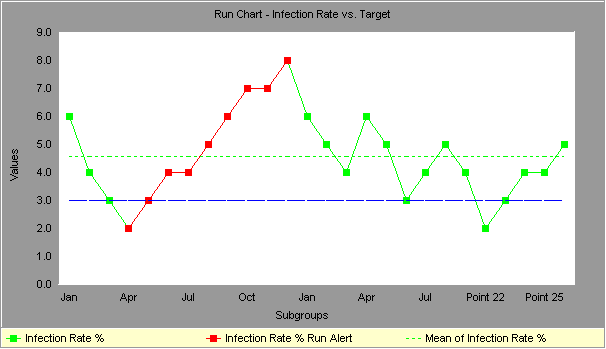
A run chart is a useful tool for visualizing data over time and identifying trends and patterns. However, understanding how to interpret the results of a run chart is crucial in extracting meaningful insights. In this section, we will discuss the process of analyzing variation and using run charts for decision-making with real-world examples.
Analyzing Variation
When interpreting run chart results, it is important to pay close attention to the variation in the data. Variation refers to the fluctuation or dispersion of data points around a mean or median. By analyzing variation in a run chart, you can identify whether the data is stable or exhibiting special cause variation.
Special cause variation occurs when a point in the chart falls outside the control limits or exhibits a notable shift or trend. This indicates that something unusual or unexpected has happened, which requires further investigation and potentially corrective action. On the other hand, if the data points fall within the control limits and exhibit random fluctuations, it indicates a stable process.
For example, let’s say you are tracking the number of customer complaints per month. If you notice a sudden spike in complaints in a particular month, that would be a point of special cause variation. It could indicate a problem with the product or service that needs immediate attention.
Using Run Charts For Decision Making
The insights gained from analyzing variation in run charts can be valuable for decision-making. By identifying special cause variation, you can take proactive measures to address issues and improve processes. Conversely, stable processes can provide confidence in the consistency and predictability of outcomes.
For example, if you are using a run chart to track the response time of your customer support team, and you observe stable data points within the control limits over a period of time, it suggests that the team is consistently meeting their targets. This information can be used to make decisions about resource allocation, performance evaluation, or process improvement initiatives.
By regularly updating and reviewing run charts, you can track the impact of any changes implemented and monitor the progress towards achieving desired outcomes. This can help drive continuous improvement and ensure that decisions are data-driven and based on objective evidence.
Credit: blog.minitab.com
Frequently Asked Questions For When To Use A Run Chart
Why Would You Use A Run Chart In Quality Improvement?
A run chart is used in quality improvement to track and analyze data over time. It helps identify trends and patterns, allowing for better decision-making and continuous improvement efforts. As a visual representation of data, it enables easy identification of variations and helps in monitoring the impact of changes.
What Is The Main Difference Between A Run Chart And A Control Chart?
A run chart tracks data over time, whereas a control chart monitors process stability by comparing data to predetermined control limits. The main difference lies in the purpose and analysis of the data.
What Is The Difference Between A Time Series Plot And A Run Chart?
A time series plot shows data over time, while a run chart displays processes and trends.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision of when to use a run chart depends on the specific circumstances and goals of your project. However, run charts can be incredibly useful in tracking trends, identifying patterns, and assessing process stability. By harnessing the power of visual representation and statistical analysis, run charts provide a clear and insightful snapshot of data over time.
Whether you are monitoring quality control measures or analyzing project performance, incorporating run charts into your toolbox can offer valuable insights and aid informed decision-making. Evidently, run charts can be a valuable asset in various industries and contexts, contributing to improved efficiency and effectiveness.